Content from Introducing Containers
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- What are containers, and why might they be useful to me?
Objectives
- Show how software depending on other software leads to configuration management problems.
- Identify the problems that software installation can pose for research.
- Explain the advantages of containerization.
- Explain how using containers can solve software configuration problems
Work in progress…
This lesson is new material that is under ongoing development. As the tools and best practices continue to develop, elements of this material are likely to evolve. We welcome any comments or suggestions on how the material can be improved or extended.
Learning about Docker Containers
The Australian Research Data Commons has produced a short introductory video about Docker containers that covers many of the points below. Watch it before or after you go through this section to reinforce your understanding!
How can software containers help your research?
Australian Research Data Commons, 2021. How can software containers help your research?. [video] Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HelrQnm3v4g DOI: http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5091260
Scientific Software Challenges
What’s Your Experience?
Take a minute to think about challenges that you have experienced in using scientific software (or software in general!) for your research. Then, share with your neighbors and try to come up with a list of common gripes or challenges.
What is a software dependency?
We will mention software dependencies a lot in this section of the workshop so it is good to clarify this term up front. A software dependency is a relationship between software components where one component relies on the other to work properly. For example, if a software application uses a library to query a database, the application depends on that library.
You may have come up with some of the following:
- you want to use software that doesn’t exist for the operating system (Mac, Windows, Linux) you’d prefer.
- you struggle with installing a software tool because you have to install a number of other dependencies first. Those dependencies, in turn, require other things, and so on (i.e. combinatoric explosion).
- the software you’re setting up involves many dependencies and only a subset of all possible versions of those dependencies actually works as desired.
- you’re not actually sure what version of the software you’re using because the install process was so circuitous.
- you and a colleague are using the same software but get different results because you have installed different versions and/or are using different operating systems.
- you installed everything correctly on your computer but now need to install it on a colleague’s computer/campus computing cluster/etc.
- you’ve written a package for other people to use but a lot of your users frequently have trouble with installation.
- you need to reproduce a research project from a former colleague and the software used was on a system you no longer have access to.
A lot of these characteristics boil down to one fact: the main program you want to use likely depends on many, many, different other programs (including the operating system!), creating a very complex, and often fragile system. One change or missing piece may stop the whole thing from working or break something that was already running. It’s no surprise that this situation is sometimes informally termed dependency hell.
Software and Science
Again, take a minute to think about how the software challenges we’ve discussed could impact (or have impacted!) the quality of your work. Share your thoughts with your neighbors. What can go wrong if our software doesn’t work?
Unsurprisingly, software installation and configuration challenges can have negative consequences for research:
- you can’t use a specific tool at all, because it’s not available or installable.
- you can’t reproduce your results because you’re not sure what tools you’re actually using.
- you can’t access extra/newer resources because you’re not able to replicate your software set up.
- others cannot validate and/or build upon your work because they cannot recreate your system’s unique configuration.
Thankfully there are ways to get underneath (a lot of) this mess: containers to the rescue! Containers provide a way to package up software dependencies and access to resources such as files and communications networks in a uniform manner.
What is a Container?
Imagine you want to install some research software but don’t want to take the chance of making a mess of your existing system by installing a bunch of additional stuff (libraries/dependencies/etc.). You don’t want to buy a whole new computer because it’s too expensive. What if, instead, you could have another independent filesystem and running operating system that you could access from your main computer, and that is actually stored within this existing computer?
More concretely, Docker Inc use the following definition of a container:
A container is a standard unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies so the application runs reliably from one computing environment to another.
https://www.docker.com/resources/what-container/
The term container can be usefully considered with reference to shipping containers. Before shipping containers were developed, packing and unpacking cargo ships was time consuming and error prone, with high potential for different clients’ goods to become mixed up. Just like shipping containers keep things together that should stay together, software containers standardize the description and creation of a complete software system: you can drop a container into any computer with the container software installed (the ‘container host’), and it should just work.
Virtualization
Containers are an example of what’s called virtualization – having a second virtual computer running and accessible from a main or host computer. Another example of virtualization are virtual machines or VMs. A virtual machine typically contains a whole copy of an operating system in addition to its own filesystem and has to get booted up in the same way a computer would. A container is considered a lightweight version of a virtual machine; underneath, the container is (usually) using the Linux kernel and simply has some flavour of Linux + the filesystem inside.
What are Docker and Singularity?
Docker and Singularity are tools that allow you to build and run containers. They are similar in many ways. However, differences in the design of Singularity and Docker mean that Singularity is particularly well-suited to running on distributed, High Performance Computing (HPC) infrastructure. System administrators will not, generally, install Docker on shared computing platforms such as lab desktops, research clusters or HPC platforms because the design of Docker presents potential security issues for shared platforms with multiple users. Singularity, on the other hand, can be run by end-users entirely within “user space”, that is, no special administrative privileges need to be assigned to a user in order for them to run and interact with containers on a platform where Singularity has been installed.
However, Singularity is more complicated to install on Windows and Mac laptops/desktops. Therefore, in this workshop, we will introduce both Docker and Singularity. We will use Docker to work locally on our own machines, and Singularity to work on the HPC.
What is the relationship between Singularity, SingularityCE and Apptainer?
Singularity is open source and was initially developed within the research community. The company Sylabs was founded in 2018 to provide commercial support for Singularity. In May 2021, Sylabs “forked” the codebase to create a new project called SingularityCE (where CE means “Community Edition”). This in effect marks a common point from which two projects—SingularityCE and Singularity—developed. Sylabs continue to develop both the free, open source SingularityCE and a Pro/Enterprise edition of the software. In November 2021, the original open source Singularity project renamed itself to Apptainer and joined the Linux Foundation.
At the time of writing, in the context of the material covered in
this lesson, Apptainer and Singularity are effectively interchangeable.
If you are working on a platform that now has Apptainer installed, you
might find that the only change you need to make when working through
this material is to use the the command apptainer instead
of singularity. This course will continue to refer to
Singularity until differences between the projects warrant choosing one
project or the other for the course material.
Container Images
One final term: while the container is an alternative filesystem layer that you can access and run from your computer, the container image is the ‘recipe’ or template for a container. The container image has all the required information to start up a running copy of the container. A running container tends to be transient and can be started and shut down. The container image is more long-lived, as a definition for the container. You could think of the container image like a cookie cutter – it can be used to create multiple copies of the same shape (or container) and is relatively unchanging, where cookies come and go. If you want a different type of container (cookie) you need a different container image (cookie cutter).
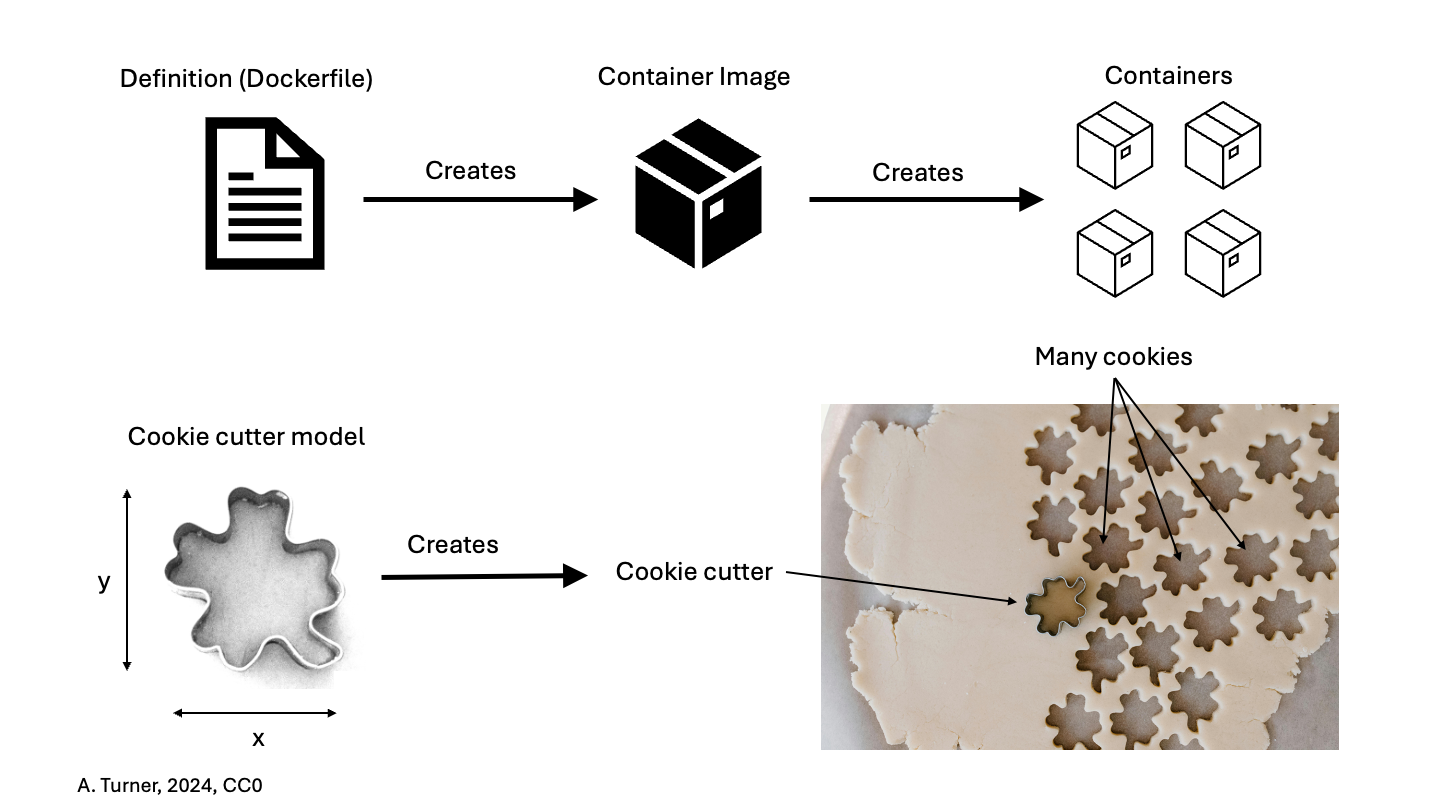
Putting the Pieces Together
Think back to some of the challenges we described at the beginning. The many layers of scientific software installations make it hard to install and re-install scientific software – which ultimately, hinders reliability and reproducibility.
But now, think about what a container is – a self-contained, complete, separate computer filesystem. What advantages are there if you put your scientific software tools into containers?
This solves several of our problems:
- documentation – there is a clear record of what software and software dependencies were used, from bottom to top.
- portability – the container can be used on any computer that has Docker installed – it doesn’t matter whether the computer is Mac, Windows or Linux-based.
- reproducibility – you can use the exact same software and environment on your computer and on other resources (like a large-scale computing cluster).
- configurability – containers can be sized to take advantage of more resources (memory, CPU, etc.) on large systems (clusters) or less, depending on the circumstances.
The rest of this workshop will show you how to download and run containers from pre-existing container images on your own computer, and how to create and share your own container images.
Use cases for containers
Now that we have discussed a little bit about containers – what they do and the issues they attempt to address – you may be able to think of a few potential use cases in your area of work. Some examples of common use cases for containers in a research context include:
- Using containers solely on your own computer to use a specific software tool or to test out a tool (possibly to avoid a difficult and complex installation process, to save your time or to avoid dependency hell).
- Creating a
Dockerfilethat generates a container image with software that you specify installed, then sharing a container image generated using this Dockerfile with your collaborators for use on their computers or a remote computing resource (e.g. cloud-based or HPC system). - Archiving the container images so you can repeat analysis/modelling using the same software and configuration in the future – capturing your workflow.
- Almost all software depends on other software components to function, but these components have independent evolutionary paths.
- Small environments that contain only the software that is needed for a given task are easier to replicate and maintain.
- Critical systems that cannot be upgraded, due to cost, difficulty, etc. need to be reproduced on newer systems in a maintainable and self-documented way.
- Virtualization allows multiple environments to run on a single computer.
- Containerization improves upon the virtualization of whole computers by allowing efficient management of the host computer’s memory and storage resources.
- Containers are built from ‘recipes’ that define the required set of software components and the instructions necessary to build/install them within a container image.
- Docker and Singularity/Apptainer are software platforms that can create containers and the resources they use.
Content from Introducing the Docker Command Line
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How do I know Docker is installed and running?
- How do I interact with Docker?
Objectives
- Explain how to check that Docker is installed and is ready to use.
- Demonstrate some initial Docker command line interactions.
- Use the built-in help for Docker commands.
Docker command line
Start the Docker application that you installed in working through the setup instructions for this session. Note that this might not be necessary if your laptop is running Linux or if the installation added the Docker application to your startup process.
You may need to login to Docker Hub
The Docker application will usually provide a way for you to log in to the Docker Hub using the application’s menu (macOS) or systray icon (Windows) and it is usually convenient to do this when the application starts. This will require you to use your Docker Hub username and your password. We will not actually require access to the Docker Hub until later in the course but if you can login now, you should do so.
Determining your Docker Hub username
If you no longer recall your Docker Hub username, e.g., because you have been logging into the Docker Hub using your email address, you can find out what it is through the steps:
- Open https://hub.docker.com/ in a web browser window
- Sign-in using your email and password (don’t tell us what it is)
- In the top-right of the screen you will see your username
Once your Docker application is running, open a shell (terminal) window, and run the following command to check that Docker is installed and the command line tools are working correctly. Below is the output for a Mac version, but the specific version is unlikely to matter much: it does not have to precisely match the one listed below.
OUTPUT
Docker version 20.10.5, build 55c4c88The above command has not actually relied on the part of Docker that runs containers, just that Docker is installed and you can access it correctly from the command line.
A command that checks that Docker is working correctly is the
docker container ls command (we cover this command in more
detail later in the course).
Without explaining the details, output on a newly installed system would likely be:
OUTPUT
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES(The command docker system info could also be used to
verify that Docker is correctly installed and operational but it
produces a larger amount of output.)
However, if you instead get a message similar to the following
OUTPUT
Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?then you need to check that you have started the Docker Desktop, Docker Engine, or however else you worked through the setup instructions.
Getting help
Often when working with a new command line tool, we need to get help.
These tools often have some sort of subcommand or flag (usually
help, -h, or --help) that
displays a prompt describing how to use the tool. For Docker, it’s no
different. If we run docker --help, we see the following
output (running docker also produces the help message):
OUTPUT
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/Users/vini/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and default context set with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/Users/vini/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/Users/vini/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/Users/vini/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
app* Docker App (Docker Inc., v0.9.1-beta3)
builder Manage builds
buildx* Build with BuildKit (Docker Inc., v0.5.1-docker)
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
image Manage images
manifest Manage Docker image manifests and manifest lists
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
scan* Docker Scan (Docker Inc., v0.6.0)
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.There is a list of commands and the end of the help message says:
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
For example, take the docker container ls command that we
ran previously. We can see from the Docker help prompt that
container is a Docker command, so to get help for that
command, we run:
OUTPUT
Usage: docker container COMMAND
Manage containers
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
inspect Display detailed information on one or more containers
kill Kill one or more running containers
logs Fetch the logs of a container
ls List containers
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
prune Remove all stopped containers
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
run Run a command in a new container
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker container COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.There’s also help for the container ls command:
OUTPUT
Usage: docker container ls [OPTIONS]
List containers
Aliases:
ls, ps, list
Options:
-a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print containers using a Go template
-n, --last int Show n last created containers (includes all states) (default -1)
-l, --latest Show the latest created container (includes all states)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Only display container IDs
-s, --size Display total file sizesYou may notice that there are many commands that stem from the
docker command. Instead of trying to remember all possible
commands and options, it’s better to learn how to effectively get help
from the command line. Although we can always search the web, getting
the built-in help from our tool is often much faster and may provide the
answer right away. This applies not only to Docker, but also to most
command line-based tools.
Docker Command Line Interface (CLI) syntax
In this lesson we use the newest Docker CLI syntax introduced
with the Docker Engine version 1.13. This new syntax combines
commands into groups you will most often want to interact with. In the
help example above you can see image and
container management commands, which can be used to
interact with your images and containers respectively. With this new
syntax you issue commands using the following pattern
docker [command] [subcommand] [additional options]
Comparing the output of two help commands above, you can see that the
same thing can be achieved in multiple ways. For example to start a
Docker container using the old syntax you would use
docker run. To achieve the same with the new syntax, you
use docker container run instead. Even though the old
approach is shorter and still officially supported, the new syntax is
more descriptive, less error-prone and is therefore recommended.
Exploring a command
Run docker --help and pick a command from the list.
Explore the help prompt for that command. Try to guess how a command
would work by looking at the Usage: section of the
prompt.
Suppose we pick the docker image build command:
OUTPUT
Usage: docker image build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
Build an image from a Dockerfile
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip)
--build-arg list Set build-time variables
--cache-from strings Images to consider as cache sources
--cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the container
--compress Compress the build context using gzip
--cpu-period int Limit the CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) period
--cpu-quota int Limit the CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) quota
-c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
-f, --file string Name of the Dockerfile (Default is 'PATH/Dockerfile')
--force-rm Always remove intermediate containers
--iidfile string Write the image ID to the file
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--label list Set metadata for an image
-m, --memory bytes Memory limit
--memory-swap bytes Swap limit equal to memory plus swap: '-1' to enable unlimited swap
--network string Set the networking mode for the RUN instructions during build (default "default")
--no-cache Do not use cache when building the image
--pull Always attempt to pull a newer version of the image
-q, --quiet Suppress the build output and print image ID on success
--rm Remove intermediate containers after a successful build (default true)
--security-opt strings Security options
--shm-size bytes Size of /dev/shm
-t, --tag list Name and optionally a tag in the 'name:tag' format
--target string Set the target build stage to build.
--ulimit ulimit Ulimit options (default [])We could try to guess that the command could be run like this:
or
Where https://github.com/docker/rootfs.git could be any
relevant URL that supports a Docker image.
- A toolbar icon indicates that Docker is ready to use (on Windows and macOS).
- You will typically interact with Docker using the command line.
- To learn how to run a certain Docker command, we can type the
command followed by the
--helpflag.
Content from Exploring and Running Containers
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How do I interact with Docker containers and container images on my computer?
Objectives
- Use the correct command to see which Docker container images are on your computer.
- Be able to download new Docker container images.
- Demonstrate how to start an instance of a container from a container image.
- Describe at least two ways to execute commands inside a running Docker container.
Reminder of terminology: container images and containers
Recall that a container image is the template from which particular instances of containers will be created.
Let’s explore our first Docker container. The Docker team provides a
simple container image online called hello-world. We’ll
start with that one.
Downloading Docker images
The docker image command is used to interact with Docker
container images. You can find out what container images you have on
your computer by using the following command (“ls” is short for
“list”):
If you’ve just installed Docker, you won’t see any container images listed.
To get a copy of the hello-world Docker container image
from the internet, run this command:
You should see output like this:
OUTPUT
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
1b930d010525: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f9dfddf63636d84ef479d645ab5885156ae030f611a56f3a7ac7f2fdd86d7e4e
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
docker.io/library/hello-world:latestDocker Hub
Where did the hello-world container image come from? It
came from the Docker Hub website, which is a place to share Docker
container images with other people. More on that in a later episode.
Exercise: Check on Your Images
What command would you use to see if the hello-world
Docker container image had downloaded successfully and was on your
computer? Give it a try before checking the solution.
Note that the downloaded hello-world container image is
not in the folder where you are in the terminal! (Run ls by
itself to check.) The container image is not a file like our normal
programs and documents; Docker stores it in a specific location that
isn’t commonly accessed, so it’s necessary to use the special
docker image command to see what Docker container images
you have on your computer.
Running the hello-world container
To create and run containers from named Docker container images you
use the docker container run command. Try the following
docker container run invocation. Note that it does not
matter what your current working directory is.
OUTPUT
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/What just happened? When we use the docker container run
command, Docker does three things:
| 1. Starts a Running Container | 2. Performs Default Action | 3. Shuts Down the Container |
|---|---|---|
| Starts a running container, based on the container image. Think of this as the “alive” or “inflated” version of the container – it’s actually doing something. | If the container has a default action set, it will perform that default action. This could be as simple as printing a message (as above) or running a whole analysis pipeline! | Once the default action is complete, the container stops running (or exits). The container image is still there, but nothing is actively running. |
The hello-world container is set up to run an action by
default – namely to print this message.
Using docker container run to get
the image
We could have skipped the docker image pull step; if you
use the docker container run command and you don’t already
have a copy of the Docker container image, Docker will automatically
pull the container image first and then run it.
Running a container with a chosen command
But what if we wanted to do something different with the container?
The output just gave us a suggestion of what to do – let’s use a
different Docker container image to explore what else we can do with the
docker container run command. The suggestion above is to
use ubuntu, but we’re going to run a different type of
Linux, alpine instead because it’s quicker to download.
Run the Alpine Docker container
Try downloading the alpine container image and using it
to run a container. You can do it in two steps, or one. What are
they?
What happened when you ran the Alpine Docker container?
If you have never used the alpine Docker container image
on your computer, Docker probably printed a message that it couldn’t
find the container image and had to download it. If you used the
alpine container image before, the command will probably
show no output. That’s because this particular container is designed for
you to provide commands yourself. Try running this instead:
You should see the output of the cat /etc/os-release
command, which prints out the version of Alpine Linux that this
container is using and a few additional bits of information.
Hello World, Part 2
Can you run a copy of the alpine container and make it
print a “hello world” message?
Give it a try before checking the solution.
So here, we see another option – we can provide commands at the end
of the docker container run command and they will execute
inside the running container.
Running containers interactively
In all the examples above, Docker has started the container, run a
command, and then immediately stopped the container. But what if we
wanted to keep the container running so we could log into it and test
drive more commands? The way to do this is by adding the interactive
flags -i and -t (usually combined as
-it) to the docker container run command and
provide a shell (bash,sh, etc.) as our
command. The alpine Docker container image doesn’t include
bash so we need to use sh.
Technically…
Technically, the interactive flag is just -i – the extra
-t (combined as -it above) is the “pseudo-TTY”
option, a fancy term that means a text interface. This allows you to
connect to a shell, like sh, using a command line. Since
you usually want to have a command line when running interactively, it
makes sense to use the two together.
Your prompt should change significantly to look like this:
That’s because you’re now inside the running container! Try these commands:
pwdlswhoamiecho $PATHcat /etc/os-release
All of these are being run from inside the running container, so
you’ll get information about the container itself, instead of your
computer. To finish using the container, type exit.
Practice Makes Perfect
Can you find out the version of Ubuntu installed on the
ubuntu container image? (Hint: You can use the same command
as used to find the version of alpine.)
Can you also find the apt-get program? What does it do?
(Hint: try passing --help to almost any command will give
you more information.)
Run an interactive ubuntu container – you can use
docker image pull first, or just run it with this
command:
OR you can get the bash shell instead
Then try, running these commands
Exit when you’re done.
Even More Options
There are many more options, besides -it that can be
used with the docker container run command! A few of them
will be covered in later episodes and
we’ll share two more common ones here:
--rm: this option guarantees that any running container is completely removed from your computer after the container is stopped. Without this option, Docker actually keeps the “stopped” container around, which you’ll see in a later episode. Note that this option doesn’t impact the container images that you’ve pulled, just running instances of containers.--name=: By default, Docker assigns a random name and ID number to each container instance that you run on your computer. If you want to be able to more easily refer to a specific running container, you can assign it a name using this option.
Conclusion
So far, we’ve seen how to download Docker container images, use them to run commands inside running containers, and even how to explore a running container from the inside. Next, we’ll take a closer look at all the different kinds of Docker container images that are out there.
- The
docker image pullcommand downloads Docker container images from the internet. - The
docker image lscommand lists Docker container images that are (now) on your computer. - The
docker container runcommand creates running containers from container images and can run commands inside them. - When using the
docker container runcommand, a container can run a default action (if it has one), a user specified action, or a shell to be used interactively.
Content from Cleaning Up Containers
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How do I interact with a Docker container on my computer?
- How do I manage my containers and container images?
Objectives
- Explain how to list running and completed containers.
- Know how to list and remove container images.
Removing images
The container images and their corresponding containers can start to take up a lot of disk space if you don’t clean them up occasionally, so it’s a good idea to periodically remove containers and container images that you won’t be using anymore.
In order to remove a specific container image, you need to find out details about the container image, specifically, the “Image ID”. For example, say my laptop contained the following container image:
OUTPUT
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest fce289e99eb9 15 months ago 1.84kBYou can remove the container image with a
docker image rm command that includes the Image
ID, such as:
or use the container image name, like so:
However, you may see this output:
OUTPUT
Error response from daemon: conflict: unable to remove repository reference "hello-world" (must force) - container e7d3b76b00f4 is using its referenced image fce289e99eb9This happens when Docker hasn’t cleaned up some of the previously running containers based on this container image. So, before removing the container image, we need to be able to see what containers are currently running, or have been run recently, and how to remove these.
What containers are running?
Working with containers, we are going to shift back to the command:
docker container. Similar to docker image, we
can list running containers by typing:
OUTPUT
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESNotice that this command didn’t return any containers because our containers all exited and thus stopped running after they completed their work.
docker ps
The command docker ps serves the same purpose as
docker container ls, and comes from the Unix shell command
ps which describes running processes.
What containers have run recently?
There is also a way to list running containers, and those that have
completed recently, which is to add the
--all/-a flag to the
docker container ls command as shown below.
OUTPUT
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9c698655416a hello-world "/hello" 2 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 minutes ago zen_dubinsky
6dd822cf6ca9 hello-world "/hello" 3 minutes ago Exited (0) 3 minutes ago eager_engelbartKeeping it clean
You might be surprised at the number of containers Docker is still
keeping track of. One way to prevent this from happening is to add the
--rm flag to docker container run. This will
completely wipe out the record of the run container when it exits. If
you need a reference to the running container for any reason,
don’t use this flag.
How do I remove an exited container?
To delete an exited container you can run the following command,
inserting the CONTAINER ID for the container you wish to
remove. It will repeat the CONTAINER ID back to you, if
successful.
OUTPUT
9c698655416aAn alternative option for deleting exited containers is the
docker container prune command. Note that this command
doesn’t accept a container ID as an option because it deletes ALL exited
containers! Be careful with this command as deleting
the container is forever. Once a container is
deleted you can not get it back. If you have containers you may
want to reconnect to, you should not use this command.
It will ask you if to confirm you want to remove these containers, see
output below. If successful it will print the full
CONTAINER ID back to you for each container it has
removed.
OUTPUT
WARNING! This will remove all stopped containers.
Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
Deleted Containers:
9c698655416a848278d16bb1352b97e72b7ea85884bff8f106877afe0210acfc
6dd822cf6ca92f3040eaecbd26ad2af63595f30bb7e7a20eacf4554f6ccc9b2bRemoving images, for real this time
Now that we’ve removed any potentially running or stopped containers,
we can try again to delete the hello-world
container image.
OUTPUT
Untagged: hello-world:latest
Untagged: hello-world@sha256:5f179596a7335398b805f036f7e8561b6f0e32cd30a32f5e19d17a3cda6cc33d
Deleted: sha256:fce289e99eb9bca977dae136fbe2a82b6b7d4c372474c9235adc1741675f587e
Deleted: sha256:af0b15c8625bb1938f1d7b17081031f649fd14e6b233688eea3c5483994a66a3The reason that there are a few lines of output, is that a given
container image may have been formed by merging multiple underlying
layers. Any layers that are used by multiple Docker container images
will only be stored once. Now the result of docker image ls
should no longer include the hello-world container
image.
-
docker containerhas subcommands used to interact and manage containers. -
docker imagehas subcommands used to interact and manage container images. -
docker container lsordocker pscan provide information on currently running containers.
Content from Singularity: Getting started
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- What is Singularity and why might I want to use it?
Objectives
- Understand what Singularity is and when you might want to use it.
- Undertake your first run of a simple Singularity container.
What is Singularity?
So far in this lesson we have been using Docker to run containers. However, the design of Docker presents potential security issues for shared computing platforms with multiple users, such as lab desktops, research clusters or HPC platforms. Therefore, system administrators will generally not install Docker on such shared platforms. Singularity, on the other hand, can be run by end-users entirely within “user space”, that is, no special administrative privileges need to be assigned to a user in order for them to run and interact with containers on a platform where Singularity has been installed.
What is the relationship between Singularity, SingularityCE and Apptainer?
Singularity is open source and was initially developed within the research community. The company Sylabs was founded in 2018 to provide commercial support for Singularity. In May 2021, Sylabs “forked” the codebase to create a new project called SingularityCE (where CE means “Community Edition”). This in effect marks a common point from which two projects—SingularityCE and Singularity—developed. Sylabs continue to develop both the free, open source SingularityCE and a Pro/Enterprise edition of the software. In November 2021, the original open source Singularity project renamed itself to Apptainer and joined the Linux Foundation.
At the time of writing, in the context of the material covered in
this lesson, Apptainer and Singularity are effectively interchangeable.
If you are working on a platform that now has Apptainer installed, you
might find that the only change you need to make when working through
this material is to use the the command apptainer instead
of singularity. This course will continue to refer to
Singularity until differences between the projects warrant choosing one
project or the other for the course material.
Getting started with Singularity
Initially developed within the research community, Singularity is open source and the repository is currently available in the “The Next Generation of High Performance Computing” GitHub organisation. This Singularity material is intended to be used on a remote platform where Singularity has been pre-installed.
If you’re attending a taught version of this course, you will be provided with access details for a remote platform made available to you. This platform will have the Singularity software pre-installed.
Sign in to the remote platform, with Singularity installed, that
you’ve been provided with access to. Check that the
singularity command is available in your terminal:
OUTPUT
singularity-ce version 4.1.2-jammyDepending on the version of Singularity installed on your system, you
may see a different version. At the time of writing, v4.2.2
is the latest release of Singularity CE and v1.3.6 is the
latest version of Apptainer.
Getting an image and running a Singularity container
If you recall from learning about Docker, Docker images are formed of
a set of layers that make up the complete image. When you pull
a Docker image from Docker Hub, you see the different layers being
downloaded to your system. They are stored in your local Docker
repository on your system and you can see details of the available
images using the docker command.
Singularity images are a little different. Singularity uses the Singularity Image Format (SIF)
and images are provided as single SIF files (with a
.sif filename extension). Singularity images can be pulled
from Singularity Hub, a
registry for container images. Singularity is also capable of running
containers based on images pulled from Docker Hub and some other sources.
We’ll look at accessing containers from Docker Hub later in the
Singularity material.
Singularity Hub
Note that in addition to providing a repository that you can pull images from, Singularity Hub can also build Singularity images for you from a recipe - a configuration file defining the steps to build an image. We’ll look at recipes and building images later.
Let’s begin by creating a test directory, changing into
it and pulling a test Hello World image from
Singularity Hub:
OUTPUT
INFO: Downloading shub image
59.75 MiB / 59.75 MiB [===============================================================================================================] 100.00% 52.03 MiB/s 1sWhat just happened?! We pulled a SIF image from Singularity Hub using
the singularity pull command and directed it to store the
image file using the name hello-world.sif in the current
directory. If you run the ls command, you should see that
the hello-world.sif file is now present in the current
directory. This is our image and we can now run a container based on
this image:
OUTPUT
RaawwWWWWWRRRR!! Avocado!The above command ran the hello-world container from the image we downloaded from Singularity Hub and the resulting output was shown.
How did the container determine what to do when we ran it?! What did running the container actually do to result in the displayed output?
When you run a container from a Singularity image without using any
additional command line arguments, the container runs the default run
script that is embedded within the image. This is a shell script that
can be used to run commands, tools or applications stored within the
image on container startup. We can inspect the image’s run script using
the singularity inspect command:
OUTPUT
#!/bin/sh
exec /bin/bash /rawr.shThis shows us the script within the hello-world.sif
image configured to run by default when we use the
singularity run command.
That concludes this introductory Singularity episode. The next episode looks in more detail at running containers.
- Singularity is another container platform and it is often used in cluster/HPC/research environments.
- Singularity has a different security model to other container platforms, one of the key reasons that it is well suited to HPC and cluster environments.
- Singularity has its own container image format (SIF).
- The
singularitycommand can be used to pull images from Singularity Hub and run a container from an image file.
Content from The Singularity cache
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- Why does Singularity use a local cache?
- Where does Singularity store images?
Objectives
- Learn about Singularity’s image cache.
- Learn how to manage Singularity images stored locally.
Singularity’s image cache
While Singularity doesn’t have a local image repository in the same
way as Docker, it does cache downloaded image files. As we saw in the
previous episode, images are simply .sif files stored on
your local disk.
If you delete a local .sif image that you have pulled
from a remote image repository and then pull it again, if the image is
unchanged from the version you previously pulled, you will be given a
copy of the image file from your local cache rather than the image being
downloaded again from the remote source. This removes unnecessary
network transfers and is particularly useful for large images which may
take some time to transfer over the network. To demonstrate this, remove
the hello-world.sif file stored in your test
directory and then issue the pull command again:
OUTPUT
INFO: Use image from cacheAs we can see in the above output, the image has been returned from the cache and we don’t see the output that we saw previously showing the image being downloaded from Singularity Hub.
How do we know what is stored in the local cache? We can find out
using the singularity cache command:
OUTPUT
There are 1 container file(s) using 62.65 MB and 0 oci blob file(s) using 0.00 kB of space
Total space used: 62.65 MBThis tells us how many container files are stored in the cache and
how much disk space the cache is using but it doesn’t tell us
what is actually being stored. To find out more information we
can add the -v verbose flag to the list
command:
OUTPUT
NAME DATE CREATED SIZE TYPE
hello-world_latest.sif 2020-04-03 13:20:44 62.65 MB shub
There are 1 container file(s) using 62.65 MB and 0 oci blob file(s) using 0.00 kB of space
Total space used: 62.65 MBThis provides us with some more useful information about the actual
images stored in the cache. In the TYPE column we can see
that our image type is shub because it’s a SIF
image that has been pulled from Singularity Hub.
Cleaning the Singularity image cache
We can remove images from the cache using the
singularity cache clean command. Running the command
without any options will display a warning and ask you to confirm that
you want to remove everything from your cache.
You can also remove specific images or all images of a particular
type. Look at the output of singularity cache clean --help
for more information.
Cache location
By default, Singularity uses $HOME/.singularity/cache as
the location for the cache. You can change the location of the cache by
setting the SINGULARITY_CACHEDIR environment variable to
the cache location you want to use.
- Singularity caches downloaded images so that an unchanged image
isn’t downloaded again when it is requested using the
singularity pullcommand. - You can free up space in the cache by removing all locally cached images or by specifying individual images to remove.
Content from Using Singularity containers to run commands
Last updated on 2025-02-18 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How do I run different commands within a container?
- How do I access an interactive shell within a container?
Objectives
- Learn how to run different commands when starting a container.
- Learn how to open an interactive shell within a container environment.
Running specific commands within a container
We saw earlier that we can use the singularity inspect
command to see the run script that a container is configured to run by
default. What if we want to run a different command within a
container?
If we know the path of an executable that we want to run within a
container, we can use the singularity exec command. For
example, using the hello-world.sif container that we’ve
already pulled from Singularity Hub, we can run the following within the
test directory where the hello-world.sif file
is located:
OUTPUT
Hello World!Here we see that a container has been started from the
hello-world.sif image and the /bin/echo
command has been run within the container, passing the input
Hello World!. The command has echoed the provided input to
the console and the container has terminated.
Note that the use of singularity exec has overriden any
run script set within the image metadata and the command that we
specified as an argument to singularity exec has been run
instead.
Basic exercise: Running a different command within the “hello-world” container
Can you run a container based on the hello-world.sif
image that prints the current date and time?
The difference between singularity run and
singularity exec
Above we used the singularity exec command. In earlier
episodes of this course we used singularity run. To
clarify, the difference between these two commands is:
singularity run: This will run the default command set for containers based on the specfied image. This default command is set within the image metadata when the image is built (we’ll see more about this in later episodes). You do not specify a command to run when usingsingularity run, you simply specify the image file name. As we saw earlier, you can use thesingularity inspectcommand to see what command is run by default when starting a new container based on an image.singularity exec: This will start a container based on the specified image and run the command provided on the command line followingsingularity exec <image file name>. This will override any default command specified within the image metadata that would otherwise be run if you usedsingularity run.
Opening an interactive shell within a container
If you want to open an interactive shell within a container,
Singularity provides the singularity shell command. Again,
using the hello-world.sif image, and within our
test directory, we can run a shell within a container from
the hello-world image:
OUTPUT
Singularity> whoami
[<your username>]
Singularity> ls
hello-world.sif
Singularity> As shown above, we have opened a shell in a new container started
from the hello-world.sif image. Note that the shell prompt
has changed to show we are now within the Singularity container.
Discussion: Running a shell inside a Singularity container
Q: What do you notice about the output of the above commands entered within the Singularity container shell?
Q: Does this differ from what you might see within a Docker container?
Use the exit command to exit from the container
shell.
- The
singularity execis an alternative tosingularity runthat allows you to start a container running a specific command. - The
singularity shellcommand can be used to start a container and run an interactive shell within it.
Content from Files in Singularity containers
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How do I make data available in a Singularity container?
- What data is made available by default in a Singularity container?
Objectives
- Understand that some data from the host system is usually made available by default within a container
- Learn more about how Singularity handles users and binds directories from the host filesystem.
The way in which user accounts and access permissions are handled in Singularity containers is very different from that in Docker (where you effectively always have superuser/root access). When running a Singularity container, you only have the same permissions to access files as the user you are running as on the host system.
In this episode we’ll look at working with files in the context of Singularity containers and how this links with Singularity’s approach to users and permissions within containers.
Users within a Singularity container
The first thing to note is that when you ran whoami
within the container shell you started at the end of the previous
episode, you should have seen the username that you were signed in as on
the host system when you ran the container.
For example, if my username were jc1000, I’d expect to
see the following:
But hang on! I downloaded the standard, public version of the
hello-world.sif image from Singularity Hub. I haven’t
customised it in any way. How is it configured with my own user
details?!
If you have any familiarity with Linux system administration, you may
be aware that in Linux, users and their Unix groups are configured in
the /etc/passwd and /etc/group files
respectively. In order for the shell within the container to know of my
user, the relevant user information needs to be available within these
files within the container.
Assuming this feature is enabled within the installation of
Singularity on your system, when the container is started, Singularity
appends the relevant user and group lines from the host system to the
/etc/passwd and /etc/group files within the
container [1].
This means that the host system can effectively ensure that you cannot access/modify/delete any data you should not be able to on the host system and you cannot run anything that you would not have permission to run on the host system since you are restricted to the same user permissions within the container as you are on the host system.
Files and directories within a Singularity container
Singularity also binds some directories from the
host system where you are running the singularity command
into the container that you’re starting. Note that this bind process is
not copying files into the running container, it is making an existing
directory on the host system visible and accessible within the container
environment. If you write files to this directory within the running
container, when the container shuts down, those changes will persist in
the relevant location on the host system.
There is a default configuration of which files and directories are bound into the container but ultimate control of how things are set up on the system where you are running Singularity is determined by the system administrator. As a result, this section provides an overview but you may find that things are a little different on the system that you’re running on.
One directory that is likely to be accessible within a container that
you start is your home directory. You may also find that the
directory from which you issued the singularity command
(the current working directory) is also mapped.
The mapping of file content and directories from a host system into a Singularity container is illustrated in the example below showing a subset of the directories on the host Linux system and in a Singularity container:
OUTPUT
Host system: Singularity container:
------------- ----------------------
/ /
├── bin ├── bin
├── etc ├── etc
│ ├── ... │ ├── ...
│ ├── group ─> user's group added to group file in container ─>│ ├── group
│ └── passwd ──> user info added to passwd file in container ──>│ └── passwd
├── home ├── usr
│ └── jc1000 ───> user home directory made available ──> ─┐ ├── sbin
├── usr in container via bind mount │ ├── home
├── sbin └────────>└── jc1000
└── ... └── ...
Questions and exercises: Files in Singularity containers
Q1: What do you notice about the ownership of files
in a container started from the hello-world image? (e.g. take a look at
the ownership of files in the root directory (/))
Exercise 1: In this container, try editing (for
example using the editor vi which should be available in
the container) the /rawr.sh file. What do you notice?
If you’re not familiar with vi there are many quick
reference pages online showing the main commands for using the editor,
for example this
one.
Exercise 2: In your home directory within the container shell, try and create a simple text file. Is it possible to do this? If so, why? If not, why not?! If you can successfully create a file, what happens to it when you exit the shell and the container shuts down?
A1: Use the ls -l command to see a
detailed file listing including file ownership and permission details.
You should see that most of the files in the / directory
are owned by root, as you’d probably expect on any Linux
system. If you look at the files in your home directory, they should be
owned by you.
A Ex1: We’ve already seen from the previous answer
that the files in / are owned by root so we
wouldn’t expect to be able to edit them if we’re not the root user.
However, if you tried to edit /rawr.sh you probably saw
that the file was read only and, if you tried for example to delete the
file you would have seen an error similar to the following:
cannot remove '/rawr.sh': Read-only file system. This tells
us something else about the filesystem. It’s not just that we don’t have
permission to delete the file, the filesystem itself is read-only so
even the root user wouldn’t be able to edit/delete this
file. We’ll look at this in more detail shortly.
A Ex2: Within your home directory, you should be able to successfully create a file. Since you’re seeing your home directory on the host system which has been bound into the container, when you exit and the container shuts down, the file that you created within the container should still be present when you look at your home directory on the host system.
Binding additional host system directories to the container
We may sometimes want to work with datasets or scripts stored in
shared locations, using the container. For example, the
/datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/ folder
contains some toy data files.
Let’s say we wanted to analyse these files using a container based on
the hello-world.sif container image.
Running containers
Question: What command would we use to run ls from the
hello-world.sif container?
If we try using the container to run ls on the shared
dataset directory, what happens?
OUTPUT
/bin/ls: cannot access /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/: No such file or directoryNo such file or directory
Question: What does the error message mean? Why might ls
inside the container not be able to find or open our directory?
This question is here for you to think about - we explore the answer to this question in the content below.
The problem here is that the container and its filesystem is separate from our host computer’s filesystem. When the container runs, it can’t see anything outside itself, apart from the files and directories we discussed above, which are bound to the container by default.
In order to access data files (outside the container, on our host computer), we need to bind that directory to the container, and create a link between the container and our host computer.
We can create a mount between our computer and the running container
by using an additional option to singularity run or
singularity exec. The option will look like this
--bind /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/:/data
What this means is: make the directory
/datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/ (on the host
computer) – the source – visible within the container that is
about to be started, and inside this container, name the directory
/data – the target.
Let’s try running the command now:
BASH
$ singularity exec --bind /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/:/data hello-world.sif ls /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/But we get the same error!
OUTPUT
/bin/ls: cannot access /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/: No such file or directoryThis final piece is a bit tricky – we really have to remember to put
ourselves inside the container. Where is the data? It’s in the directory
that’s been mapped to /data – so we need to include that in
the path to ls. This command should give us what we
need:
BASH
$ singularity exec --bind /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/:/data hello-world.sif ls /dataNote that if we create any files in the /data directory
while the container is running, these files will appear on our host
filesystem in the original directory and will stay there even when the
container stops.
Note that you don’t need to specify a target mount location in the container. By default, a bind is mounted at the same path in the container as on the host system. So we could also use this command:
BASH
$ singularity exec --bind /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/ hello-world.sif ls /datasets/hpc_training/sample-files/arrayjob/You can also specify multiple binds to --bind by
separating them by commas (,).
You can also copy data into a container image at build time if there is some static data required in the image. We cover this later in the section on building containers.
Exercise - binding directories
Bind the /datasets/hpc_training/ directory into the
hello-world.sif container. Can you run the
“helloworld.py” script found in
/datasets/hpc_training/utils/?
References
[1] Gregory M. Kurzer, Containers for Science, Reproducibility and Mobility: Singularity P2. Intel HPC Developer Conference, 2017. Available at: https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/presentation/hpc-containers-singularity-advanced.pdf
- Your current directory and home directory are usually available by default in a container.
- You have the same username and permissions in a container as on the host system.
- You can specify additional host system directories to be available in the container.
Content from Using Docker images with Singularity
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How do I use Docker images with Singularity?
Objectives
- Learn how to run Singularity containers based on Docker images.
Using Docker images with Singularity
Singularity can also start containers directly from Docker images, opening up access to a huge number of existing container images available on Docker Hub and other registries.
While Singularity doesn’t actually run a container using the Docker image (it first converts it to a format suitable for use by Singularity), the approach used provides a seamless experience for the end user. When you direct Singularity to run a container based on pull a Docker image, Singularity pulls the slices or layers that make up the Docker image and converts them into a single-file Singularity SIF image.
For example, moving on from the simple Hello World examples
that we’ve looked at so far, let’s pull one of the official Docker Python
images. We’ll use the image with the tag
3.9.6-slim-buster which has Python 3.9.6 installed on
Debian’s Buster
(v10) Linux distribution:
OUTPUT
INFO: Converting OCI blobs to SIF format
INFO: Starting build...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob 33847f680f63 done
Copying blob b693dfa28d38 done
Copying blob ef8f1a8cefd1 done
Copying blob 248d7d56b4a7 done
Copying blob 478d2dfa1a8d done
Copying config c7d70af7c3 done
Writing manifest to image destination
Storing signatures
2021/07/27 17:23:38 info unpack layer: sha256:33847f680f63fb1b343a9fc782e267b5abdbdb50d65d4b9bd2a136291d67cf75
2021/07/27 17:23:40 info unpack layer: sha256:b693dfa28d38fd92288f84a9e7ffeba93eba5caff2c1b7d9fe3385b6dd972b5d
2021/07/27 17:23:40 info unpack layer: sha256:ef8f1a8cefd144b4ee4871a7d0d9e34f67c8c266f516c221e6d20bca001ce2a5
2021/07/27 17:23:40 info unpack layer: sha256:248d7d56b4a792ca7bdfe866fde773a9cf2028f973216160323684ceabb36451
2021/07/27 17:23:40 info unpack layer: sha256:478d2dfa1a8d7fc4d9957aca29ae4f4187bc2e5365400a842aaefce8b01c2658
INFO: Creating SIF file...Note how we see singularity saying that it’s “Converting OCI blobs to SIF format”. We then see the layers of the Docker image being downloaded and unpacked and written into a single SIF file. Once the process is complete, we should see the python-3.9.6.sif image file in the current directory.
We can now run a container from this image as we would with any other singularity image.
Running the Python 3.9.6 image that we just pulled from Docker Hub
Try running the Python 3.9.6 image. What happens?
Try running some simple Python statements…
This should put you straight into a Python interactive shell within the running container:
Python 3.9.6 (default, Jul 22 2021, 15:24:21)
[GCC 8.3.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> Now try running some simple Python statements:
In addition to running a container and having it run the default run script, you could also start a container running a shell in case you want to undertake any configuration prior to running Python. This is covered in the following exercise:
Open a shell within a Python container
Try to run a shell within a singularity container based on the
python-3.9.6.sif image. That is, run a container that opens
a shell rather than the default Python interactive console as we saw
above. See if you can find more than one way to achieve this.
Within the shell, try starting the Python interactive console and running some Python commands.
Recall from the earlier material that we can use the
singularity shell command to open a shell within a
container. To open a regular shell within a container based on the
python-3.9.6.sif image, we can therefore simply run:
OUTPUT
Singularity> echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
Singularity> cat /etc/issue
Debian GNU/Linux 10 \n \l
Singularity> python
Python 3.9.6 (default, Jul 22 2021, 15:24:21)
[GCC 8.3.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> print('Hello World!')
Hello World!
>>> exit()
Singularity> exit
$ It is also possible to use the singularity exec command
to run an executable within a container. We could, therefore, use the
exec command to run /bin/bash:
OUTPUT
Singularity> echo $SHELL
/bin/bashYou can run the Python console from your container shell simply by
running the python command.
References
\[1\] Gregory M. Kurzer, Containers for Science, Reproducibility and Mobility: Singularity P2. Intel HPC Developer Conference, 2017. Available at: https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/presentation/hpc-containers-singularity-advanced.pdf
- Singularity can start a container from a Docker image which can be pulled directly from Docker Hub.
Content from Finding Containers on Docker Hub
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- What is the Docker Hub, and why is it useful?
Objectives
- Understand the importance of container registries such as Docker Hub, quay.io, etc.
- Explore the Docker Hub webpage for a popular Docker container image.
- Find the list of tags for a particular Docker container image.
- Identify the three components of a container image’s identifier.
In the previous episode, we ran a few different containers derived
from different container images: hello-world,
alpine, and maybe ubuntu for Docker
containers, and hello-world.sif for Singularity. Where did
these container images come from? Container repositories - namely the Docker Hub and the (archive-only) Singularity
Hub.
Introducing the Docker Hub
The Docker Hub is an online repository of container images, a vast number of which are publicly available. A large number of the container images are curated by the developers of the software that they package. Also, many commonly used pieces of software that have been containerized into images are officially endorsed, which means that you can trust the container images to have been checked for functionality, stability, and that they don’t contain malware.
Docker can be used without connecting to the Docker Hub
Note that while the Docker Hub is well integrated into Docker functionality, the Docker Hub is certainly not required for all types of use of Docker containers. For example, some organizations may run container infrastructure that is entirely disconnected from the Internet.
Exploring an Example Docker Hub Page
As an example of a Docker Hub page, let’s explore the page for the
official Python language container images. The most basic form of
containerized Python is in the python container image
(which is endorsed by the Docker team). Open your web browser to https://hub.docker.com/_/python
to see what is on a typical Docker Hub software page.
The top-left provides information about the name, short description, popularity (i.e., more than a billion downloads in the case of this container image), and endorsements.
The top-right provides the command to pull this container image to your computer.
The main body of the page contains many used headings, such as:
- Which tags (i.e., container image versions) are supported;
- Summary information about where to get help, which computer architectures are supported, etc.;
- A longer description of the container image;
- Examples of how to use the container image; and
- The license that applies.
The “How to use the image” section of most container images’ pages will provide examples that are likely to cover your intended use of the container image.
Exploring Container Image Versions
A single Docker Hub page can have many different versions of
container images, based on the version of the software inside. These
versions are indicated by “tags”. When referring to the specific version
of a container image by its tag, you use a colon, :, like
this:
CONTAINER_IMAGE_NAME:TAGSo if I wanted to download the python container image,
with Python 3.8, I would use this name:
Or to download the image with Singularity, I would run:
But if I wanted to download a Python 3.6 container image, I would use this name:
Or to download the image with Singularity, I would run:
The default tag (which is used if you don’t specify one) is called
latest.
So far, we’ve only seen container images that are maintained by the Docker team. However, it’s equally common to use container images that have been produced by individual owners or organizations. Container images that you create and upload to Docker Hub would fall into this category, as would the container images maintained by organizations like ContinuumIO (the folks who develop the Anaconda Python environment) or community groups like rocker, a group that builds community R container images.
The name for these group- or individually-managed container images have this format:
OWNER/CONTAINER_IMAGE_NAME:TAGRepositories
The technical name for the contents of a Docker Hub page is a “repository.” The tag indicates the specific version of the container image that you’d like to use from a particular repository. So a slightly more accurate version of the above example is:
OWNER/REPOSITORY:TAGWhat’s in a name?
How would I download the Docker container image produced by the
rocker group that has version 3.6.1 of R and the tidyverse
installed?
Note: the container image described in this exercise is large and
won’t be used later in this lesson, so you don’t actually need to pull
the container image – constructing the correct docker pull
or singularity pull command is sufficient.
First, search for rocker in Docker Hub. Then look for
their tidyverse container image. You can look at the list
of tags, or just guess that the tag is 3.6.1. Altogether,
that means that the name of the container image we want to download
is:
or to use this image on an HPC system with Singularity installed:
Finding Container Images on Docker Hub
There are many different container images on Docker Hub. This is where the real advantage of using containers shows up – each container image represents a complete software installation that you can use and access without any extra work!
The easiest way to find container images is to search on Docker Hub, but sometimes software pages have a link to their container images from their home page.
Note that anyone can create an account on Docker Hub and share container images there, so it’s important to exercise caution when choosing a container image on Docker Hub. These are some indicators that a container image on Docker Hub is consistently maintained, functional and secure:
- The container image is updated regularly.
- The container image associated with a well established company, community, or other group that is well-known.
- There is a Dockerfile or other listing of what has been installed to the container image.
- The container image page has documentation on how to use the container image.
If a container image is never updated, created by a random person, and does not have a lot of metadata, it is probably worth skipping over. Even if such a container image is secure, it is not reproducible and not a dependable way to run research computations.
What container image is right for you?
Find a Docker container image that’s relevant to you. Take into account the suggestions above of what to look for as you evaluate options. If you’re unsuccessful in your search, or don’t know what to look for, you can use the R or Python container image we’ve already seen.
Once you find a container image, use the skills from the previous
episode to download the container image and explore it. You can use
either docker on your laptop, or singularity
on the HPC to do this.
- The Docker Hub is an online repository of container images.
- Many Docker Hub container images are public, and may be officially endorsed.
- Each Docker Hub page about a container image provides structured information and subheadings
- Most Docker Hub pages about container images contain sections that provide examples of how to use those container images.
- Many Docker Hub container images have multiple versions, indicated by tags.
- The naming convention for Docker container images is:
OWNER/CONTAINER_IMAGE_NAME:TAG - You can pull images from Docker Hub using both Docker and Singularity.
Content from Creating Your Own Container Images
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How can I make my own Docker container images?
- How do I document the ‘recipe’ for a Docker container image?
Objectives
- Explain the purpose of a
Dockerfileand show some simple examples. - Demonstrate how to build a Docker container image from a
Dockerfile. - Compare the steps of creating a container image interactively versus
a
Dockerfile. - Create an installation strategy for a container image.
- Demonstrate how to upload (‘push’) your container images to the Docker Hub.
- Describe the significance of the Docker Hub naming scheme.
There are lots of reasons why you might want to create your own Docker container image.
- You can’t find a container image with all the tools you need on Docker Hub.
- You want to have a container image to “archive” all the specific software versions you ran for a project.
- You want to share your workflow with someone else.
Interactive installation
Before creating a reproducible installation, let’s experiment with
installing software inside a container. Start a container from the
alpine container image we used before, interactively:
Because this is a basic container, there’s a lot of things not
installed – for example, python3.
OUTPUT
sh: python3: not foundInside the container, we can run commands to install Python 3. The
Alpine version of Linux has a installation tool called apk
that we can use to install Python 3.
We can test our installation by running a Python command:
Exercise: Searching for Help
Can you find instructions for installing R on Alpine Linux? Do they work?
Once we exit, these changes are not saved to a new container image by
default. There is a command that will “snapshot” our changes, but
building container images this way is not easily reproducible. Instead,
we’re going to take what we’ve learned from this interactive
installation and create our container image from a reproducible recipe,
known as a Dockerfile.
If you haven’t already, exit out of the interactively running container.
Put installation instructions in a Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a plain text file with keywords and
commands that can be used to create a new container image.
From your shell, go to the folder you downloaded at the start of the lesson and print out the Dockerfile inside:
OUTPUT
FROM <EXISTING IMAGE>
RUN <INSTALL CMDS FROM SHELL>
CMD <CMD TO RUN BY DEFAULT>Let’s break this file down:
- The first line,
FROM, indicates which container image we’re starting with. It is the “base” container image we are going to start from. - The next two lines
RUN, will indicate installation commands we want to run. These are the same commands that we used interactively above. - The last line,
CMD, indicates the default command we want a container based on this container image to run, if no other command is provided. It is recommended to provideCMDin exec-form (see theCMDsection of the Dockerfile documentation for more details). It is written as a list which contains the executable to run as its first element, optionally followed by any arguments as subsequent elements. The list is enclosed in square brackets ([]) and its elements are double-quoted (") strings which are separated by commas. For example,CMD ["ls", "-lF", "--color", "/etc"]would translate tols -lF --color /etc.
shell-form and exec-form for CMD
Another way to specify the parameter for the CMD
instruction is the shell-form. Here you type the command as
you would call it from the command line. Docker then silently runs this
command in the image’s standard shell. CMD cat /etc/passwd
is equivalent to CMD ["/bin/sh", "-c", "cat /etc/passwd"].
We recommend to prefer the more explicit exec-form because we
will be able to create more flexible container image command options and
make sure complex commands are unambiguous in this format.
Exercise: Take a Guess
Do you have any ideas about what we should use to fill in the sample Dockerfile to replicate the installation we did above?
Based on our experience above, edit the Dockerfile (in
your text editor of choice) to look like this:
FROM alpine
RUN apk add --update python3 py3-pip python3-dev
CMD ["python3", "--version"]The recipe provided by the Dockerfile shown in the
solution to the preceding exercise will use Alpine Linux as the base
container image, add Python 3, the pip package management tool and some
additional Python header files, and set a default command to request
Python 3 to report its version information.
Create a new Docker image
So far, we only have a text file named Dockerfile – we
do not yet have a container image. We want Docker to take this
Dockerfile, run the installation commands contained within
it, and then save the resulting container as a new container image. To
do this we will use the docker image build command.
We have to provide docker image build with two pieces of
information:
- the location of the
Dockerfile - the name of the new container image. Remember the naming scheme from
before? You should name your new image with your Docker Hub username and
a name for the container image, like this:
USERNAME/CONTAINER_IMAGE_NAME.
All together, the build command that you should run on your computer, will have a similar structure to this:
The -t option names the container image; the final dot
indicates that the Dockerfile is in our current
directory.
For example, if my user name was alice and I wanted to
call my container image alpine-python, I would use this
command:
Build Context
Notice that the final input to docker image build isn’t
the Dockerfile – it’s a directory! In the command above, we’ve used the
current working directory (.) of the shell as the final
input to the docker image build command. This option
provides what is called the build context to Docker – if there
are files being copied into the built container image more details in the next episode
they’re assumed to be in this location. Docker expects to see a
Dockerfile in the build context also (unless you tell it to look
elsewhere).
Even if it won’t need all of the files in the build context directory, Docker does “load” them before starting to build, which means that it’s a good idea to have only what you need for the container image in a build context directory, as we’ve done in this example.
Exercise: Review!
Think back to earlier. What command can you run to check if your container image was created successfully? (Hint: what command shows the container images on your computer?)
We didn’t specify a tag for our container image name. What tag did Docker automatically use?
What command will run a container based on the container image you’ve created? What should happen by default if you run such a container? Can you make it do something different, like print “hello world”?
To see your new image, run
docker image ls. You should see the name of your new container image under the “REPOSITORY” heading.In the output of
docker image ls, you can see that Docker has automatically used thelatesttag for our new container image.We want to use
docker container runto run a container based on a container image.
The following command should run a container and print out our default message, the version of Python:
To run a container based on our container image and print out “Hello world” instead:
While it may not look like you have achieved much, you have already effected the combination of a lightweight Linux operating system with your specification to run a given command that can operate reliably on macOS, Microsoft Windows, Linux and on the cloud!
Boring but important notes about installation
There are a lot of choices when it comes to installing software – sometimes too many! Here are some things to consider when creating your own container image:
- Start smart, or, don’t install everything from scratch! If you’re using Python as your main tool, start with a Python container image. Same with the R programming language. We’ve used Alpine Linux as an example in this lesson, but it’s generally not a good container image to start with for initial development and experimentation because it is a less common distribution of Linux; using Ubuntu, Debian and CentOS are all good options for scientific software installations. The program you’re using might recommend a particular distribution of Linux, and if so, it may be useful to start with a container image for that distribution.
- How big? How much software do you really need to install? When you have a choice, lean towards using smaller starting container images and installing only what’s needed for your software, as a bigger container image means longer download times to use.
-
Know (or Google) your Linux. Different
distributions of Linux often have distinct sets of tools for installing
software. The
apkcommand we used above is the software package installer for Alpine Linux. The installers for various common Linux distributions are listed below:- Ubuntu:
aptorapt-get - Debian:
deb - CentOS:
yumMost common software installations are available to be installed via these tools. A web search for “install X on Y Linux” is usually a good start for common software installation tasks; if something isn’t available via the Linux distribution’s installation tools, try the options below.
- Ubuntu:
-
Use what you know. You’ve probably used commands
like
piporinstall.packages()before on your own computer – these will also work to install things in container images (if the basic scripting language is installed). - README. Many scientific software tools have a README or installation instructions that lay out how to install software. You want to look for instructions for Linux. If the install instructions include options like those suggested above, try those first.
In general, a good strategy for installing software is:
- Make a list of what you want to install.
- Look for pre-existing container images.
- Read through instructions for software you’ll need to install.
- Try installing everything interactively in your base container – take notes!
- From your interactive installation, create a
Dockerfileand then try to build the container image from that.
Share your new container image on Docker Hub
Container images that you release publicly can be stored on the
Docker Hub for free. If you name your container image as described
above, with your Docker Hub username, all you need to do is run the
opposite of docker image pull –
docker image push.
Make sure to substitute the full name of your container image!
In a web browser, open https://hub.docker.com, and on your user page you should now see your container image listed, for anyone to use or build on.
Logging In
Technically, you have to be logged into Docker on your computer for
this to work. Usually it happens by default, but if
docker image push doesn’t work for you, run
docker login first, enter your Docker Hub username and
password, and then try docker image push again.
What’s in a name? (again)
You don’t have to name your containers images using the
USERNAME/CONTAINER_IMAGE_NAME:TAG naming scheme. On your
own computer, you can call container images whatever you want, and refer
to them by the names you choose. It’s only when you want to share a
container image that it needs the correct naming format.
You can rename container images using the
docker image tag command. For example, imagine someone
named Alice has been working on a workflow container image and called it
workflow-test on her own computer. She now wants to share
it in her alice Docker Hub account with the name
workflow-complete and a tag of v1. Her
docker image tag command would look like this:
She could then push the re-named container image to Docker Hub, using
docker image push alice/workflow-complete:v1
Pull and run a Docker image using Singularity
Pair up with your neighbour, and pull each other’s images from Docker Hub to run with Singularity.
-
Dockerfiles specify what is within Docker container images. - The
docker image buildcommand is used to build a container image from aDockerfile. - You can share your Docker container images through the Docker Hub so that others can create Docker containers from your container images.
Content from Creating More Complex Container Images
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How can I add local files (e.g. data files) into container images at build time?
- How can I access files stored on the host system from within a running Docker container?
Objectives
- Explain how you can include files within Docker container images when you build them.
- Explain how you can access files on the Docker host from your Docker containers.
In order to create and use your own container images, you may need more information than our previous example. You may want to use files from outside the container, that are not included within the container image, either by copying the files into the container image, or by making them visible within a running container from their existing location on your host system. You may also want to learn a little bit about how to install software within a running container or a container image. This episode will look at these advanced aspects of running a container or building a container image. Note that the examples will get gradually more and more complex – most day-to-day use of containers and container images can be accomplished using the first 1–2 sections on this page.
In a previous episode, we learnt how to bind a directory using Singularity. Binding (also called mounting) a directory can be very useful when you want to run the software inside your container on many different input files. In other situations, you may want to save or archive an authoritative version of your data by adding it to the container image permanently.
First, we’ll look at how to mount directories using Docker.
Using scripts and files from outside the container
In your shell, change to the sum folder in the
docker-intro folder and look at the files inside.
This folder has both a Dockerfile and a Python script
called sum.py. Let’s say we wanted to try running the
script using a container based on our recently created
alpine-python container image.
Running containers
Question: What command would we use to run Python from the
alpine-python container?
We can run a container from the alpine-python container image using:
What happens? Since the Dockerfile that we built this
container image from had a CMD entry that specified
["python3", "--version"], running the above command simply
starts a container from the image, runs the
python3 --version command and exits. You should have seen
the installed version of Python printed to the terminal.
Instead, if we want to run an interactive Python terminal, we can use
docker container run to override the default run command
embedded within the container image. So we could run:
The -it tells Docker to set up and interactive terminal
connection to the running container, and then we’re telling Docker to
run the python3 command inside the container which gives us
an interactive Python interpreter prompt. (type exit()
to exit!)
If we try running the container and Python script, what happens?
OUTPUT
python3: can't open file '//sum.py': [Errno 2] No such file or directoryUnlike Singularity containers, Docker containers and their filesystems are completely separate from our host computer’s filesystem. When the container runs, it can’t see anything outside itself, including any of the files in our current working directory, which would be bound by default when working with Singularity.
In order to use Python (inside the container) to run our script (outside the container, on our host computer), we need to create a link between the directory on our computer and the container. When working with Docker we typically call this link a “mount”.
We can create a mount between our computer and the running container
by using an additional option to docker container run.
We’ll also use the variable ${PWD} which will substitute in
our current working directory. The option will look like this:
--mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/temp
What this means is: make my current working directory (on the host
computer) – the source – visible within the container that is
about to be started, and inside this container, name the directory
/temp – the target.
Types of mounts
You will notice that we set the mount type=bind, there
are other types of mount that can be used in Docker
(e.g. volume and tmpfs). We do not cover other
types of mounts or the differences between these mount types in the
course as it is more of an advanced topic. You can find more information
on the different mount types in the Docker
documentation.
Let’s try running the command now:
BASH
$ docker container run --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/temp alice/alpine-python python3 /temp/sum.pyWhere is the sum.py file? It’s in the directory that’s
been mapped to /temp – so we need to include that in the
path to the script. If you forget to include the path, you will see the
following error:
OUTPUT
python3: can't open file '//sum.py': [Errno 2] No such file or directoryNote that if we create any files in the /temp directory
while the container is running, these files will appear on our host
filesystem in the original directory and will stay there even when the
container stops.
Other Commonly Used Docker Run Flags
Docker run has many other useful flags to alter its function. A
couple that are commonly used include -w and
-u.
The --workdir/-w flag sets the working
directory a.k.a. runs the command being executed inside the directory
specified. For example, the following code would run the
pwd command in a container started from the latest ubuntu
image in the /home/alice directory and print
/home/alice. If the directory doesn’t exist in the image it
will create it.
docker container run -w /home/alice/ ubuntu pwdThe --user/-u flag lets you specify the
username you would like to run the container as. This is helpful if
you’d like to write files to a mounted folder and not write them as
root but rather your own user identity and group. A common
example of the -u flag is
--user $(id -u):$(id -g) which will fetch the current
user’s ID and group and run the container as that user.
Exercise: Explore the script
What happens if you use the docker container run command
above and put numbers after the script name?
This script comes from the Python Wiki and is set to add all numbers that are passed to it as arguments.
Exercise: Checking the options
Our Docker command has gotten much longer! Can you go through each piece of the Docker command above and explain what it does? How would you characterize the key components of a Docker command?
Here’s a breakdown of each piece of the command above
-
docker container run: use Docker to run a container -
--mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/temp: connect my current working directory (${PWD}) as a folder inside the container called/temp -
alice/alpine-python: name of the container image to use to run the container -
python3 /temp/sum.py: what commands to run in the container
More generally, every Docker command will have the form:
docker [action] [docker options] [docker container image] [command to run inside]
Exercise: Interactively working with mounts
Try using the directory mount option but run the container interactively. Can you find the folder that’s connected to your host computer? What’s inside?
The docker command to run the container interactively is:
Once inside, you should be able to navigate to the /temp
folder and see that’s contents are the same as the files on your host
computer:
Mounting a directory can be very useful when you want to run the software inside your container on many different input files. In other situations, you may want to save or archive an authoritative version of your data by adding it to the container image permanently. That’s what we will cover next.
Including your scripts and data within a container image
Our next project will be to add our own files to a container image –
something you might want to do if you’re sharing a finished analysis or
just want to have an archived copy of your entire analysis including the
data. Let’s assume that we’ve finished with our sum.py
script and want to add it to the container image itself.
In your shell, you should still be in the sum folder in
the docker-intro folder.
Let’s add a new line to the Dockerfile we’ve been using
so far to create a copy of sum.py. We can do so by using
the COPY keyword.
COPY sum.py /homeThis line will cause Docker to copy the file from your computer into the container’s filesystem. Let’s build the container image like before, but give it a different name:
The Importance of Command Order in a Dockerfile
When you run docker image build it executes the build in
the order specified in the Dockerfile. This order is
important for rebuilding and you typically will want to put your
RUN commands before your COPY commands.
Docker builds the layers of commands in order. This becomes important
when you need to rebuild container images. If you change layers later in
the Dockerfile and rebuild the container image, Docker
doesn’t need to rebuild the earlier layers but will instead used a
stored (called “cached”) version of those layers.
For example, in an instance where you wanted to copy
multiply.py into the container image instead of
sum.py. If the COPY line came before the
RUN line, it would need to rebuild the whole image. If the
COPY line came second then it would use the cached
RUN layer from the previous build and then only rebuild the
COPY layer.
Exercise: Did it work?
Can you remember how to run a container interactively? Try that with this one. Once inside, try running the Python script.
This COPY keyword can be used to place your own scripts
or own data into a container image that you want to publish or use as a
record. Note that it’s not necessarily a good idea to put your scripts
inside the container image if you’re constantly changing or editing
them. Then, referencing the scripts from outside the container is a good
idea, as we did in the previous section. You also want to think
carefully about size – if you run docker image ls you’ll
see the size of each container image all the way on the right of the
screen. The bigger your container image becomes, the harder it will be
to easily download.
Security Warning
Login credentials including passwords, tokens, secure access tokens or other secrets must never be stored in a container. If secrets are stored, they are at high risk to be found and exploited when made public.
Copying alternatives
Another trick for getting your own files into a container image is by
using the RUN keyword and downloading the files from the
internet. For example, if your code is in a GitHub repository, you could
include this statement in your Dockerfile to download the latest version
every time you build the container image:
RUN git clone https://github.com/alice/mycodeSimilarly, the wget command can be used to download any
file publicly available on the internet:
RUN wget ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/2.10.0/ncbi-blast-2.10.0+-x64-linux.tar.gzNote that the above RUN examples depend on commands
(git and wget respectively) that must be
available within your container: Linux distributions such as Alpine may
require you to install such commands before using them within
RUN statements.
More fancy Dockerfile options (optional, for
presentation or as exercises)
We can expand on the example above to make our container image even more “automatic”. Here are some ideas:
Make the sum.py script run automatically
FROM alpine
RUN apk add --update python3 py3-pip python3-dev
COPY sum.py /home
# Run the sum.py script as the default command
CMD ["python3", "/home/sum.py"]Build and test it:
You’ll notice that you can run the container without arguments just
fine, resulting in sum = 0, but this is boring. Supplying
arguments however doesn’t work:
results in
OUTPUT
docker: Error response from daemon: OCI runtime create failed:
container_linux.go:349: starting container process caused "exec:
\"10\": executable file not found in $PATH": unknown.This is because the arguments 10 11 12 are interpreted
as a command that replaces the default command given by
CMD ["python3", "/home/sum.py"] in the image.
To achieve the goal of having a command that always runs
when a container is run from the container image and can be
passed the arguments given on the command line, use the keyword
ENTRYPOINT in the Dockerfile.
FROM alpine
RUN apk add --update python3 py3-pip python3-dev
COPY sum.py /home
# Run the sum.py script as the default command and
# allow people to enter arguments for it
ENTRYPOINT ["python3", "/home/sum.py"]
# Give default arguments, in case none are supplied on
# the command-line
CMD ["10", "11"]Build and test it:
BASH
$ docker image build -t alpine-sum:v2 .
# Most of the time you are interested in the sum of 10 and 11:
$ docker container run alpine-sum:v2
# Sometimes you have more challenging calculations to do:
$ docker container run alpine-sum:v2 12 13 14Overriding the ENTRYPOINT
Sometimes you don’t want to run the image’s ENTRYPOINT.
For example if you have a specialized container image that does only
sums, but you need an interactive shell to examine the container:
will yield
OUTPUT
Please supply integer argumentsYou need to override the ENTRYPOINT statement in the
container image like so:
Add the sum.py script to the PATH so you
can run it directly:
FROM alpine
RUN apk add --update python3 py3-pip python3-dev
COPY sum.py /home
# set script permissions
RUN chmod +x /home/sum.py
# add /home folder to the PATH
ENV PATH /home:$PATHBuild and test it:
Best practices for writing Dockerfiles
Take a look at Nüst et al.’s “Ten simple rules
for writing Dockerfiles for reproducible data science” [1] for
some great examples of best practices to use when writing Dockerfiles.
The GitHub
repository associated with the paper also has a set of example
Dockerfiles demonstrating how the rules highlighted by
the paper can be applied.
[1] Nüst D, Sochat V, Marwick B, Eglen SJ, Head T, et al. (2020) Ten simple rules for writing Dockerfiles for reproducible data science. PLOS Computational Biology 16(11): e1008316. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008316
- Docker allows containers to read and write files from the Docker host.
- You can include files from your Docker host into your Docker
container images by using the
COPYinstruction in yourDockerfile.
Content from Containers in Research Workflows: Reproducibility and Granularity
Last updated on 2025-01-27 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How can I use container images to make my research more reproducible?
- How do I incorporate containers into my research workflow?
Objectives
- Understand how container images can help make research more reproducible.
- Understand what practical steps I can take to improve the reproducibility of my research using containers.
Although this workshop is titled “Reproducible computational environments using containers”, so far we have mostly covered the mechanics of using Docker and Singularity with only passing reference to the reproducibility aspects. In this section, we discuss these aspects in more detail.
Work in progress…
Note that reproducibility aspects of software and containers are an active area of research, discussion and development so are subject to many changes. We will present some ideas and approaches here but best practices will likely evolve in the near future.
Reproducibility
By reproducibility here we mean the ability of someone else (or your future self) being able to reproduce what you did computationally at a particular time (be this in research, analysis or something else) as closely as possible, even if they do not have access to exactly the same hardware resources that you had when you did the original work.
What makes this especially important? With research being increasingly digital in nature, more and more of our research outputs are a result of the use of software and data processing or analysis. With complex software stacks or groups of dependencies often being required to run research software, we need approaches to ensure that we can make it as easy as possible to recreate an environment in which a given research process was undertaken. There many reasons why this matters, one example being someone wanting to reproduce the results of a publication in order to verify them and then build on that research.
Some examples of why containers are an attractive technology to help with reproducibility include:
- The same computational work can be run seamlessly on different operating systems (e.g. Windows, macOS, Linux).
- You can save the exact process that you used for your computational work (rather than relying on potentially incomplete notes).
- You can save the exact versions of software and their dependencies in the container image.
- You can provide access to legacy versions of software and underlying dependencies which may not be generally available any more.
- Depending on their size, you can also potentially store a copy of key data within the container image.
- You can archive and share a container image as well as associating a persistent identifier with it, to allow other researchers to reproduce and build on your work.
Sharing images
As we have already seen, the Docker Hub provides a platform for sharing container images publicly. Once you have uploaded a container image, you can point people to its public location and they can download and build upon it.
This is fine for working collaboratively with container images on a day-to-day basis but the Docker Hub is not a good option for long-term archiving of container images in support of research and publications as:
- free accounts have a limit on how long a container image will be hosted if it is not updated
- it does not support adding persistent identifiers to container images
- it is easy to overwrite tagged container images with newer versions by mistake.
Archiving and persistently identifying container images using Zenodo
When you publish your work or make it publicly available in some way it is good practice to make container images that you used for computational work available in an immutable, persistent way and to have an identifier that allows people to cite and give you credit for the work you have done. Zenodo is one service that provides this functionality.
Zenodo supports the upload of tar archives and we can
capture our Docker container images as tar archives using the
docker image save command. For example, to export the
container image we created earlier in this lesson:
These tar container images can become quite large and Zenodo supports uploads up to 50GB so you may need to compress your archive to make it fit on Zenodo using a tool such as gzip (or zip):
Once you have your archive, you can deposit it on Zenodo and this will:
- Create a long-term archive snapshot of your Docker container image which people (including your future self) can download and reuse or reproduce your work.
- Create a persistent DOI (Digital Object Identifier) that you can cite in any publications or outputs to enable reproducibility and recognition of your work.
In addition to the archive file itself, the deposit process will ask you to provide some basic metadata to classify the container image and the associated work.
Note that Zenodo is not the only option for archiving and generating persistent DOIs for container images. There are other services out there – for example, some organizations may provide their own, equivalent, service.
Reproducibility good practice
- Make use of container images to capture the computational environment required for your work.
- Decide on the appropriate granularity for the container images you will use for your computational work – this will be different for each project/area. Take note of accepted practice from contemporary work in the same area. What are the right building blocks for individual container images in your work?
- Document what you have done and why – this can be put in comments in
the
Dockerfileand the use of the container image described in associated documentation and/or publications. Make sure that references are made in both directions so that the container image and the documentation are appropriately linked. - When you publish work (in whatever way) use an archiving and DOI service such as Zenodo to make sure your container image is captured as it was used for the work and that it is assigned a persistent DOI to allow it to be cited and referenced properly.
- Make use of tags when naming your container images, this ensures that if you update the image in future, previous versions can be retained within a container repository to be easily accessed, if this is required.
- A built and archived container image can ensure a persistently
bundled set of software and dependecies. However, a
Dockerfileprovides a lightweight means of storing a container definition that can be used to re-create a container image at a later time. If you’re taking this approach, ensure that you specify software package and dependency versions within yourDockerfilerather than just specifying package names which will generally install the most up-to-date version of a package. This may be incompatible with other elements of your software stack. Also note that storing only aDockerfilepresents reproducibility challenges because required versions of packages may not be available indefinitely, potentially meaning that you’re unable to reproduce the required environment and, hence, the research results.
Container Granularity
As mentioned above, one of the decisions you may need to make when containerising your research workflows is what level of granularity you wish to employ. The two extremes of this decision could be characterized as:
- Create a single container image with all the tools you require for your research or analysis workflow
- Create many container images each running a single command (or step) of the workflow and use them together
Of course, many real applications will sit somewhere between these two extremes.
Positives and negatives
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the two approaches to container granularity for research workflows described above? Think about this and write a few bullet points for advantages and disadvantages for each approach in the course Etherpad.
This is not an exhaustive list but some of the advantages and disadvantages could be:
Single large container image
- Advantages:
- Simpler to document
- Full set of requirements packaged in one place
- Potentially easier to maintain (though could be opposite if working with large, distributed group)
- Disadvantages:
- Could get very large in size, making it more difficult to distribute
- Could use Docker multi-stage build to reduce size
- May end up with same dependency issues within the container image from different software requirements
- Potentially more complex to test
- Less re-useable for different, but related, work
- Could get very large in size, making it more difficult to distribute
Multiple smaller container images
- Advantages:
- Individual components can be re-used for different, but related, work
- Individual parts are smaller in size making them easier to distribute
- Avoid dependency issues between different pieces of software
- Easier to test
- Disadvantage:
- More difficult to document
- Potentially more difficult to maintain (though could be easier if working with large, distributed group)
- May end up with dependency issues between component container images if they get out of sync
Next steps with containers
Now that we’re at the end of the lesson material, take a moment to reflect on what you’ve learned, how it applies to you, and what to do next.
- In your own notes, write down or diagram your understanding of Docker containers and container images: concepts, commands, and how they work.
- In the workshop’s shared notes document, write down how you think you might use containers in your daily work. If there’s something you want to try doing with containers right away, what is a next step after this workshop to make that happen?
- Container images allow us to encapsulate the computation (and data) we have used in our research.
- Using a service such as Docker Hub allows us to easily share computational work we have done.
- Using container images along with a DOI service such as Zenodo allows us to capture our work and enables reproducibility.
